Highly leveraged firms or leveraged buyouts (lbos) leveraged buyout (lbo) a leveraged buyout (lbo). Apv is an appropriate measure of value for many situations, including:
Ns Spirit Apv Method
The discount rate used in the first part is the return on assets or return on equity if unlevered;

Tax shield formula apv. To do this, we assume that the primary benefit of borrowing is a tax benefit and that. How to calculate adjusted present value (apv) to determine the. In the adjusted preset value (apv) approach the value of the firm is estimated in following steps.
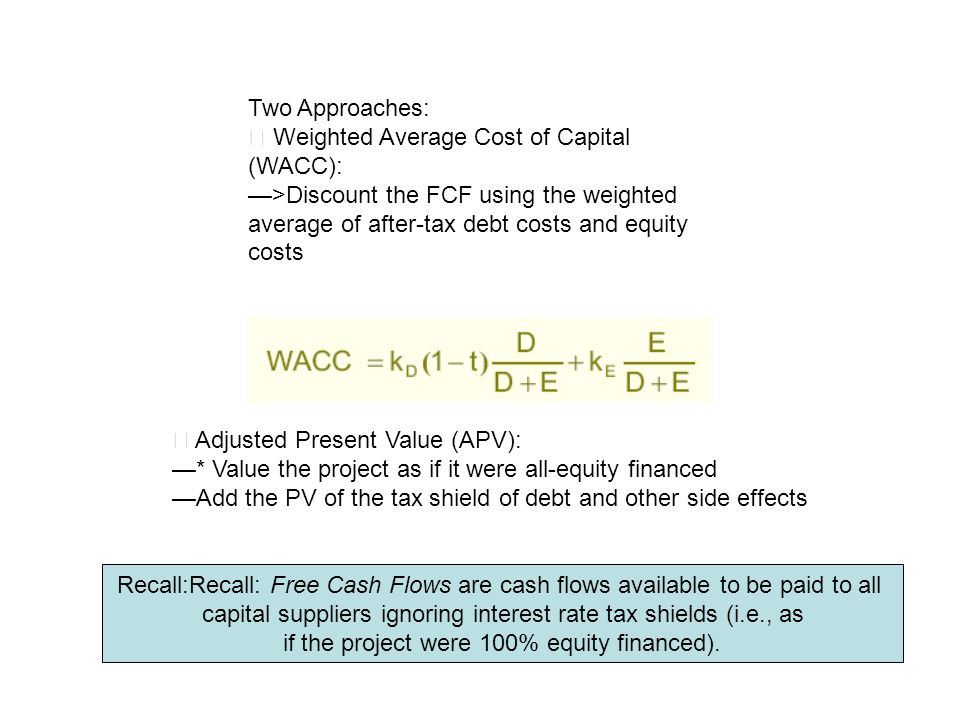
• adjusted present value (apv): Apv breaks down the value of a project into its fundamental components and thus provides useful information needed to refine the transaction and monitor its execution. With a target d/e ratio the wacc method is more convenient) constant d/e.
Apv vs discounted cash flow though there is not much difference between adjusted present value and discounted cash flow, adjusted present cash flow does not include taxes or any other financing impacts in a weighted average. C = net initial investment t = corporate tax rate k = discount rate or time value of money d = maximum rate of capital cost allowance 2. The net effect of debt includes adjustments such as the present value of interest tax shields, debt issuance costs, financial distress costs, and other financial side effects.
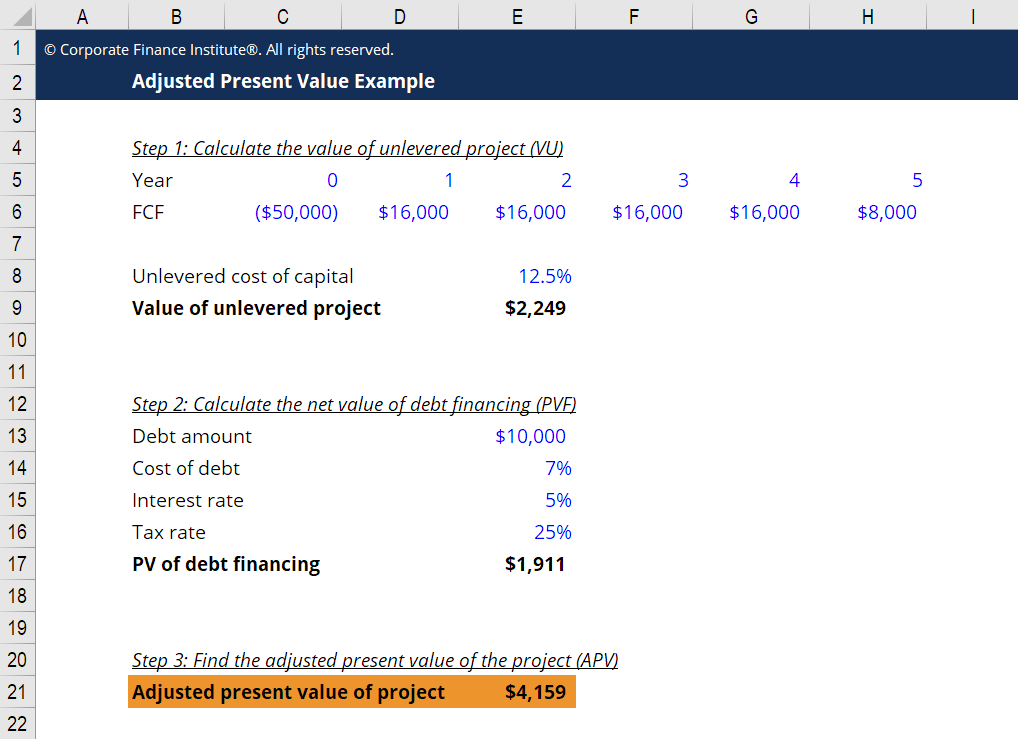
Present value of tax shield for amortizable assets present value of total tax shield from cca for a new asset acquired after november 20, 2018 𝐶𝑑𝑇1 +1.5𝑘 = ( ) (𝑑+𝑘) 1+𝑘 notation for above formula: The formula for adjusted present value is:. When calculating apv, the present values of the interest tax shields actually used in each projected year, along with the present value of the terminal value (tv) of the its, are added to the present values of future free cash flows.
The formula for apv is as follows: Therefore, apv will be $115,000, that is the sum of fcf and terminal value and interest tax shield ($100,000 + $15,000). The idea of the paper is then to use the methods of derivative pricing, namely the martingale approach, for calculating the tax shield.
As we add debt to the firm, we consider the net effect on value by considering both the benefits and the costs of borrowing. The interest tax shield can be calculated by multiplying the interest amount by the tax rate. Mathematically, it is represented as,
Present value of cash flows formula and calculations; To this end, the tax shield itself is a derivative of the unlevered firm value. The apv formula is the sum of the present value of cash flows and present value of tax shield, where present value of cash flows and tax shield is calculated separately with a different formula.
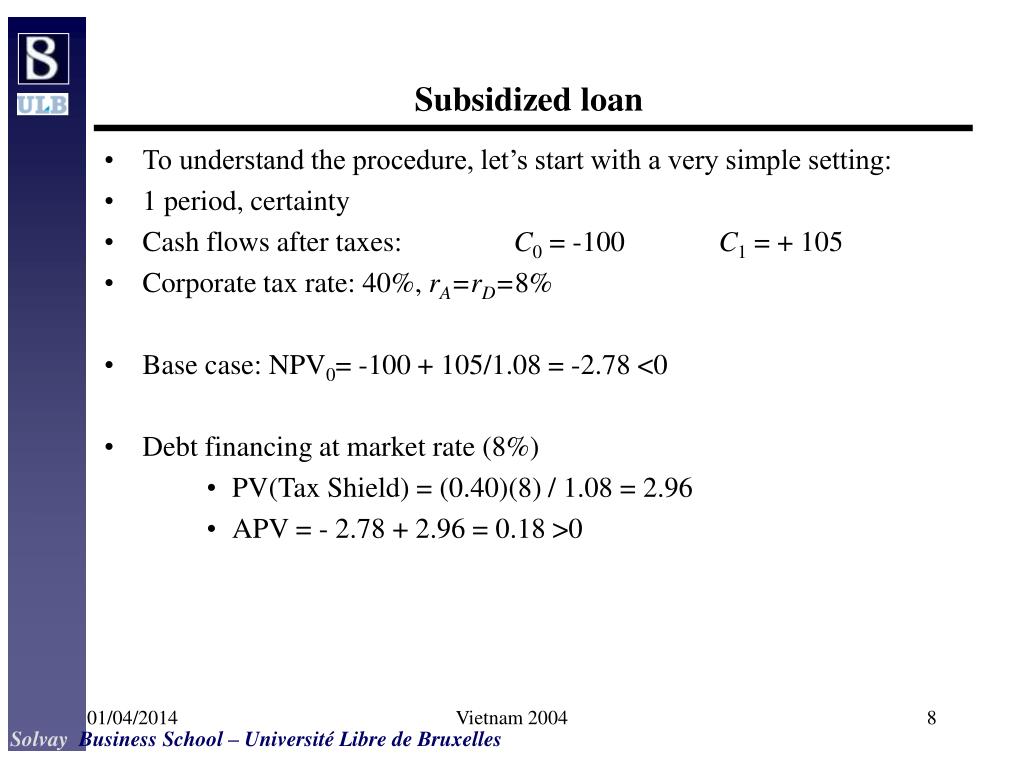
The first step is to estimate the value of a company with no leverage by calculating a npv at the cost of equity as the. The adjusted present value ( apv) is : Apv = unlevered npv of free cash flows and assumed terminal value + npv of interest tax shield and assumed terminal value:
The discount rate used in the second part is. Free cash flows are cash flows available to be paid to all capital suppliers ignoring interest rate tax shields (i.e., as. The present value of the interest tax shield is therefore calculated as:
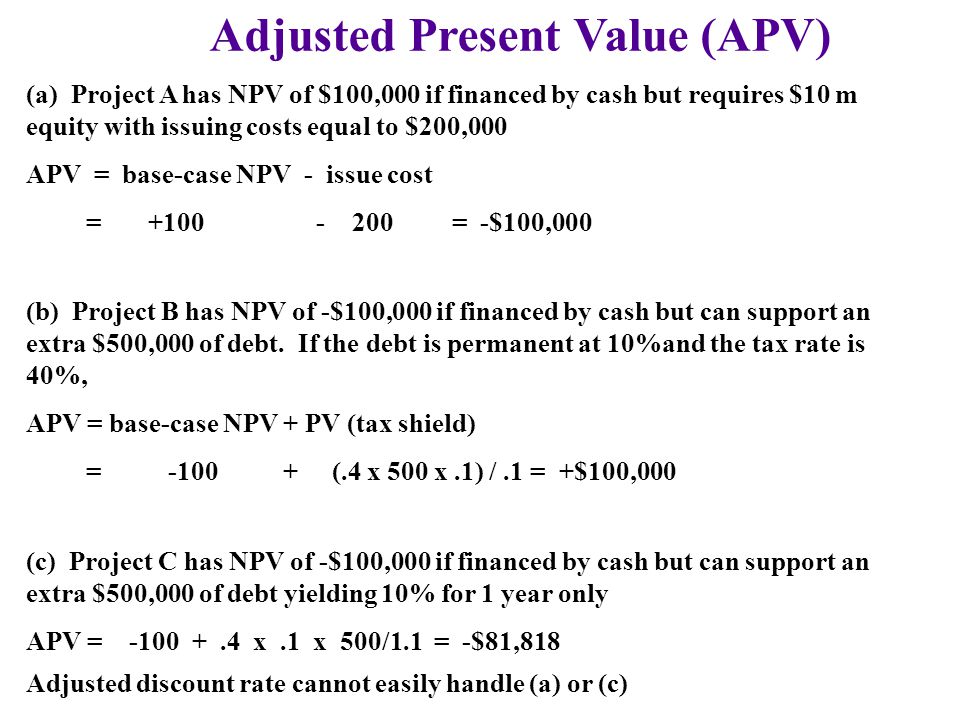
Under the apv technique then, savings would normally increase base npv. The adjusted present value approach. Npv (of a venture financed solely with equity capital) + pv of financing.
The apv method is most useful when evaluating companies or projects with a fixed debt schedule, as it can easily accommodate the side effects of financing such as interest tax shields. Pv of cash flow calculation involves cash flow, risk rate, asset beta, market return and risk rate. Pv of cash flow calculation involves cash flow, risk rate, asset beta, market return and risk rate.
In the adjusted present value (apv) approach, we begin with the value of the firm without debt. The tax shield is defined as the value of the tax savings of interest payments associated with the firm. So it tax shields normally should added back to it.
The apv formula is the sum of the present value of cash flows and present value of tax shield, where present value of cash flows and tax shield is calculated separately with a different formula. (tax rate * debt load * interest rate) / interest rate. Interest tax shield = interest expense x tax rate thereby, the apv approach allows us to see whether adding more debt results in a tangible increase (or decrease) in value, as.
The tax shield could be called also “tax savings” and in investment appraisal, this constitues a cash inflow generated from capital allowances due to investing in tax allowable capital expenditure (capex). Tax shield formula tax shield refers to the deduction allowed on the taxable income that eventually results in the reduction of taxes owed to the government. The present value of tax shield ( pv ts) is :

Capital Budgeting And Valuation With Leverage P V

Pdf The Adjusted Present Value The Combined Impact Of Growth And The Tax Shield Of Debt On The Cost Of Capital And Systematic Risk Semantic Scholar

Using Apv A Better Tool For Valuing Operations

Adjusted Present Value Apv Formula And Calculation Example - Wall Street Prep
Wacc And Apv - Ppt Video Online Download

Chapter 6 Frameworks For Valuation Adjusted Present Value Apv Instructors Please Do Not Post Raw Powerpoint Files On Public Website Thank You Ppt Download

Chapter 18

Using Apv A Better Tool For Valuing Operations

Fin 40153 Advanced Corporate Finance Basic Valuation Techniques

Chapter 18
Interactions Of Investment And Financing Decisions - Ppt Video Online Download

Adjusted Present Value Apv Formula And Calculation Example - Wall Street Prep

Apv Adjusted Present Value - Overview Components Steps

Using Apv A Better Tool For Valuing Operations

Ppt - Chapter 21 Powerpoint Presentation Free Download - Id4710282

173 Formulaic Valuation Methods Apv And Wacc - Corporate Finance
Adjusted Present Value Apv - Definition Explanation Examples
Ppt - Corporate Finance Financing And Valuation Powerpoint Presentation - Id540390

Chapter 18